9-Box Model
Summary Definition: A grid-based assessment methodology used to plot and track the performance of employees compared to their peers.
What is the 9-Box Grid Model?
The 9-box grid model is a standard workforce management framework that assesses the value of individual employees and how they compare to the rest of the team.
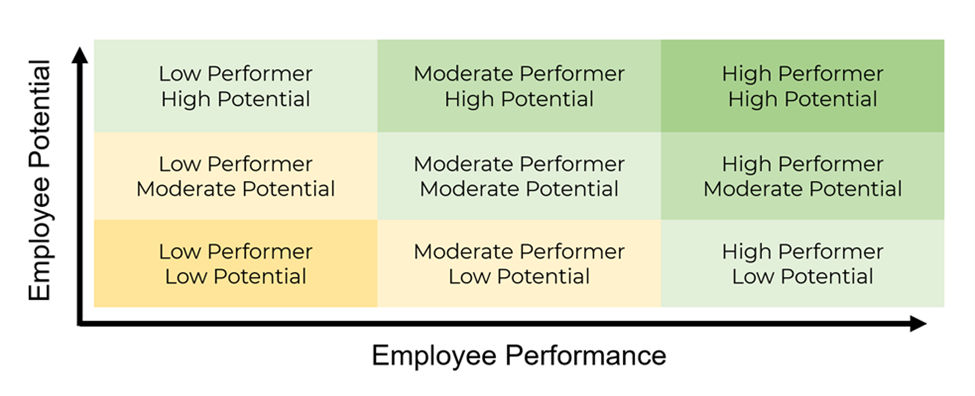
Managers determine each staff member’s performance and potential performance and plot the results onto a 9-box matrix. The resulting grid is divided into three layers, each representing a "step up" in attainment.
This splits a workforce into nine segments. "High performers" or "bad hires" are in the most extreme corners, and "core employees" are in the middle.
Analyzing the grid can help management develop career path strategies for each group, such as promoting, retraining, or terminating an employee’s contract.
Key Takeaways
- The 9-box grid model is a performance evaluation tool that can pinpoint the most and least effective employees.
- Results of the method can be used to develop career progression and training plans.
- The 9-box grid is simple, user-friendly, holistic, and cost-efficient. But it can be rigid, lacks an objective ranking method, and is prone to bias.
How Do You Create a 9-Box Grid?
To make a simple 9-box grid, draw lines to create three rows of three columns. Label the vertical rows "Employee Potential" and the horizontal columns "Employee Performance."
Here's an example of a 9-box grid:
How to Score Employees
The exact scoring rubric will differ per company, but these are some common assessment methods:
- Objective metrics: Employees are ranked by quantifiable performance indicators related to productivity.
- Managerial assessments: Supervisors can also add their opinion on factors like communication or teamwork skills.
- Peer reviews: An employee’s colleagues can rate how well the individual collaborates in a team setting.
Business Benefits of the 9-Box Assessment Model
The 9-box model can help businesses with strategic workforce planning.
For example, teams with the strongest performers will have the highest proportion of employees in the top-right segment of the 9-box grid.
On the contrary, a large concentration of employees in the bottom-left corner indicates a low-performing team/department.
Businesses can use this data to promote top talent, remove low-potential underperformers, or reorganize a talent pool by pairing leaders with high-potential underperformers as part of a mentorship scheme.
Use Cases for the 9-Box Model
The 9-box employee segmentation method is versatile and has various use cases for businesses. Some of the most common include:
- Employee engagement: Once a team has been split into segments, a company can create engagement strategies tailored to each group's needs.
- Career development: This data can be used to set realistic goals and targets for employees and to earmark high-performers for an early promotion (a process known as "employee journey mapping").
- Teambuilding: The 9-box method can also be used to create more balanced teams with a mixture of leaders, high-performers, core employees, and prospects.
- Skills gap analysis: Areas for improvement and skills a team may lack can be identified.
- Succession planning: This information can be used to plan for the future by allocating key roles to the highest performers.
Pros and Cons of the 9-Box Model
Like any model, the 9-box assessment method has advantages and disadvantages as a talent management tool. Here’s pros and cons to consider:
The Pros
- Speed: The 9-box grid is considered simple and user-friendly. Employees are assessed, and then the results are mapped on a standard template.
- Ease of use: The 9-box method takes a holistic approach to employee reviews rather than focusing on a single aspect of performance. It can be used to create tailored career paths for staff, which can improve team morale and help with retaining talent.
- Cost-efficiency: An informal 9-box method deployment is inexpensive and doesn't require much time or resources.
The Cons
- Rigidity: The 9-box model reduces employee achievements to a single label. An employee could miss opportunities if they are designated a "moderate performer" instead of a "high performer."
- Metrics: There’s no set method for ranking employees in a 9-box matrix. The HR department must create a system considered fair.
- Bias: Personal preferences regarding how to measure employee performance may skew results depending on who creates the 9-box grid.
Level Up Employee Performance
Help your employees unlock their true potential with modern performance management tools. From goal management to personalized performance review and Journals, our solutions facilitate transparent, two-communication and get your workforce involved in their own development. Employees want to grow and expect ongoing support - give it to them with Performance Management from Paylocity.